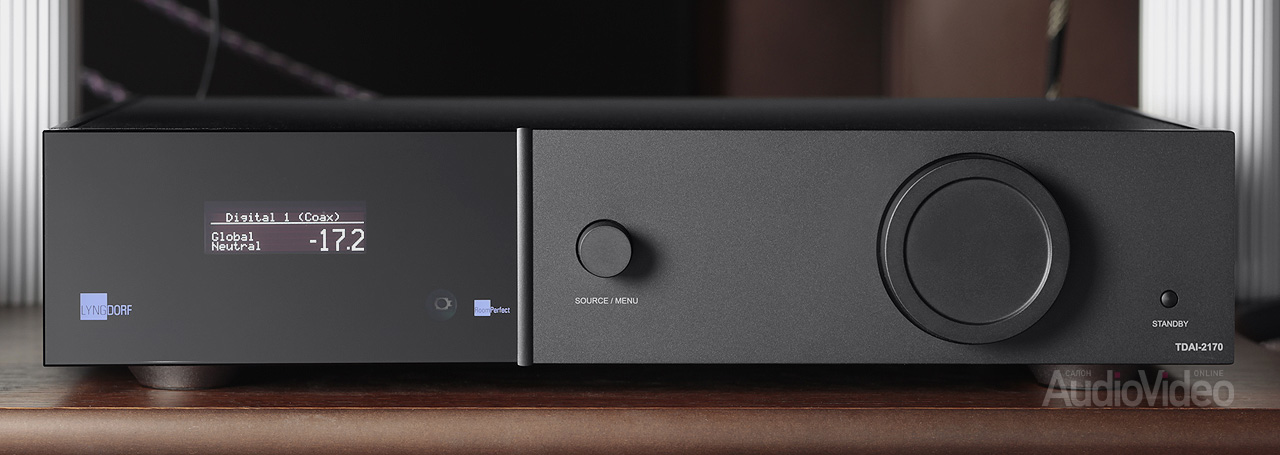
Dane Peter Lingdorf created his first digital amplifier in the late 90s - the sensational TacT Millennium. The recent development of the TDAI-2170 inherited the main principle from it - a direct path without unnecessary transformations and feedback. And in addition, it provides the modern user with a number of additional options.
And you can choose from this range yourself, because thanks to the modular design, the amplifier can be configured to suit each specific system... But we will come back to this later, now we will consider the basic equipment of the TDAI-2170, its core.
If we talk about the audio path, then in a very simplified form it can be described as follows: the PCM input format is directly modulated into a PWM (pulse width modulation) signal, which controls the powerful output MOSFET switches. Wherein analog signal formed directly at the speaker output terminals.

In fact, the path is a little more complicated - it has a DSP on which several Lyngdorf proprietary solutions are implemented. The most interesting thing is the correction system Rooms Room Perfect, which has a number of important differences from the widespread Audessy, Dirac, MCACC, etc. First, it has two tuning modes - Focus1 and Focus2. In the first case, the sound field is optimized for one listener, and in the second, for a small audience. Moreover, Room Perfect not only aligns frequency response while eliminating the effects of standing waves, it also minimizes phase interference. The latter circumstance affects the formation of the sound stage, therefore, two focusing modes are introduced. If desired, Room Perfect can be turned off by setting the Bypass mode. The second important point is that to improve the measurement accuracy, the microphone can (and should) be placed in several places in the room under study. And if the complete information about the acoustic characteristics of the room is taken as 100%, then when measured from four points it will be 95%, and from seven points - 99%. Here's how Room Perfect works in practice.
Room Perfect not only flattens the frequency response, eliminating the effects of standing waves, but also minimizes phase interference.
Another unique technology from the Danish company, Intersample Clipping Correction (ICC), is able to restore the original waveform at its peaks if the input audio file was recorded at 0 dBFS or above. This, by the way, is a real problem, since many modern hi-cuts are created on the principle of "the louder the better". In fact, this level is not acceptable for all DACs - even if the level reaches -0.5 dBFS at the peaks, noticeable distortion may appear during upsampling. So, the ICC algorithm detects such fragments and eliminates clipping by slightly lowering the overall volume level, but it restores the full dynamic range of the original recording.

The final amplifier develops a power of 2 x 170 W at 4 Ohms with a distortion of 0.07%, while the entire device weighs only 8 kg. Agree that such mass-energy indicators are unrealistic for traditional AB amplifiers. Low distortion is due to the fact that the clock frequency of the PWM is increased to 400 kHz - today this is a record figure for pulse power supplies. In addition, as the manufacturer points out, there are no sources of internal noise in the TDAI-2170 path, which causes dead silence in pauses. This property is called "Blackground". And, as I already mentioned, all the listed parameters are obtained without general feedback.
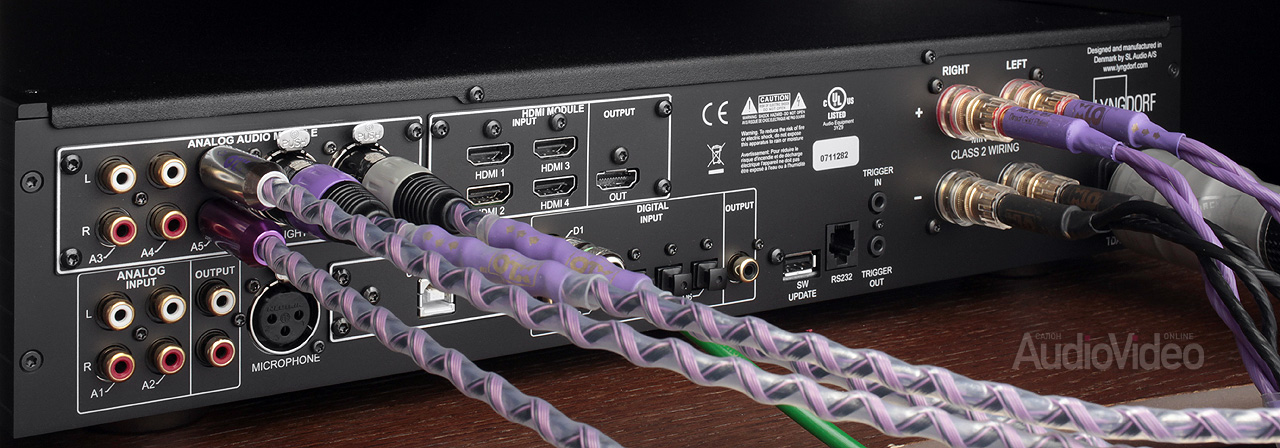
The modules installed in the amplifier are plug-n-play activated thanks to advanced software. Perhaps the main addition is a USB converter with asynchronous "B" input, capable of accepting PCM with a resolution of up to 32 bits / 384 kHz, as well as audio in DSD64 and DSD128 streams. All of this is reproduced without intermediate conversion to analog form, as happens in conventional class D amplifiers.

The second module is perhaps the most unusual for a stereophonic device. It contains four HDMI 1.4 inputs and the same output, making the amplifier a true multimedia control center. The most interesting thing is that these interfaces are not implemented on standard chipsets at all and are intended, incl. for high quality digital audio transmission. With this configuration, an AV receiver is no longer needed if you do not intend to build a multi-channel configuration. In addition, today's Smart TV is becoming a networked source of high definition content, and the addition of HDMI is a smart move.
Intersample Clipping Correction (ICC) technology is able to restore the original waveform at its peaks if the input audio file was recorded at or above 0 dBFS.
And finally, the third module is intended for audiophile connection via analog inputs. It contains one balanced (XLR) stereo input and three conventional RCA inputs.
The basic version provides a pair of RCA line inputs, a pair of coaxial and four optical Toslinks.

The rear panel also contains 12-volt trigger jacks, an RS-232 port, a USB A interface for firmware upgrades, and four screw-type speaker terminals.
Lyngdorf components have always had a distinctly futuristic style, and the TDAI-2170 is no exception. Thanks to the efforts of the designers, the amplifier visually appears to be smaller than it actually is. The avant-garde style of the front panel meets the notions of the aesthetics of a modern digital device: there are only two three-dimensional objects on the mirror plane - a small knob responsible for selecting an input / navigating through the menu and a dominant volume control. This is a digital encoder with a very fine pitch - you need to make several turns to change the level by one decibel. On the dot display on the left, service information is displayed in several lines and in very large - the set volume value.
The amplifier is controlled by means of a narrow stylish remote control.
![]()
For testing the TDAI-2170, we chose a solid three-band Opera Grand Callas acoustics. We start listening in Room Perfect Focus1 mode after careful tuning with the stock microphone. Accordingly, I will tell you about the construction of space first. On different CDs, the sound stage, of course, differs, but in each case you can understand how it was seen by the sound engineer, who mixed this or that phonogram. In most cases, it is perfectly ordered, slightly pulled towards the center, and only separate sounds can be tied to acoustics. The third dimension is expressed quite clearly, on separate discs the background goes a meter and a half behind the front line. If you listen not from a given point, but a little from the side, then virtual sources can be distributed among the channels, leaving the middle of the stage empty. This will not happen if you switch to Focus 2 mode, it makes it possible to move around the room within some limits. When the Room Perfect processor is bypassed, the scene becomes less orderly, the musicians seem to be scattered around the stage, but the overall impression is that the sound becomes lighter, more open and free. Which is quite understandable - multi-stage data processing stopped, but early reflections began to participate in the creation of the picture. And this is in a prepared listening room with competent acoustic processing, in less favorable conditions artifacts would be much more noticeable.

But the most interesting thing about the TDAI-2170 is the reproduction of sharp spikes in the level. At almost any volume, the amplifier retains the correct dynamic scale of the original recording: quiet sounds are not ignored, pauses between sounds are really "black", and sharp peaks are accompanied by powerful bursts of energy. On some tracks with a wide dynamic range, it feels like an expander is on. Of the "digital" features, I would like to note the tendency to paint a musical picture with somewhat larger strokes, as if drawing the listener's attention to some nuances.
At any volume, the amplifier retains the correct dynamic scale of the original recording: quiet sounds are not ignored, pauses between sounds are really "black"
The tonal balance is perfect, but for a muffled room, I would recommend a vertebra acoustics, with titanium, for example, or even ribbon tweeters. In the latter case, there is no need to be afraid of rigidity and "dirt", the upper range of the TDAI-2170 is extremely clean and transparent.

The bass is not tiresome and fast enough. The movements of the diffusers are free, on sharp low notes their displacement is frighteningly large, and at the same time there are no disruptions in the transmission of the general rhythmic structure. The amplifier is fast enough and has no obvious genre preferences. It is curious that in the sound there is neither strict academicism, nor attempts to rearrange musical accents at their own discretion. And after an hour and a half of listening, there was neither fatigue, nor a feeling of discomfort - the sound is captivating, time flies by.

Lyngdorf Audio TDAI-2170
Producer: Lyngdorf Audio (Denmark)
www.lyngdorf.com
Analog Inputs: 2 x RCA, XLR || Digital inputs: 2 x RCA, 4 x Toslink, 4 x HDMI 1.4a, USB A || Nominal output power(4 Ohms: 2 x 170 W || Peak output current: 30 A || Frequency amplification range (+ 0.3 / -1.5 dB): 20 Hz - 20 kHz || Distortion at peak power: 0.07 % || Complete set: remote control, measuring microphone, network cable || Dimensions: 450 x 100 x 360 mm || Weight: 8 kg || Price for a complete set: 390000 rub.
On some tracks with a wide dynamic range, it feels like an expander is on.
- CD-player Roksan Kandy
- Streamer Cary Audio DMS-500
- Acoustic systems Opera Grand Callas
- Cables
- interconnect XLO UltraPlus UP1A RCA, XLO UltraPlus UP2A XLR
- acoustic XLO UltraPlus UP1A U12SG
The editors would like to thank the Moscow Salon Hi-Fi for their help with the audition.
The number is coming.
Listening Direct Digital Amplifier with feedback – NADM2.
Introduction.
The question of which analog or digital amplifier sounds better has haunted fans of pure sound since the first digital devices... But, until recently, most of these devices were not digital in their pure form.
But progress does not stand still, and at the end of 2009 a significant event took place, the company NAD on the market, a fully digital integrated amplifier was released NAD M2. And in this review I will tell you about his work.
Equipment.
Actually, the principle of operation of a digital amplifier has been known since the last century. This type of device is interesting in that it allows you to process and amplify the signal directly in digital form, bypassing the intermediate stage of digital-to-analog conversion. However, let's talk about this in more detail.
So, a digital audio signal from any source, be it CD transport or DVD the player is fed to the amplifier in digital form. Further, in a conventional digital amplifier, it comes to the board DSP processor for decoding and processing sound and transmitted to a high-quality DAC, where it is converted to analog form, then amplified in an amplifier and fed to a speaker system. Here is a simplified example of a digital amplifier with an analog output gain stage. As you can see, there are several stages that can distort the original signal. Of course it's a fee DSP , DAC and analog processing path. Each of these nodes is ready to add noise, interference and other "joys" to the audio signal.
A completely different path lies ahead for digital music in NAD M 2. Here, the input signal encoded in PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) format goes directly to the digital signal processor board ( DSP ). Note that the processor carries out data processing strictly in digital form. Then the signal is converted from PCM to PWM ( pulse width modulation). Again, this operation is performed digitally just before the amplification that occurs on the field effect transistors.
Processed and amplified signal enters a powerful pulse stage, at the output of which a high-quality analog filter is used for conversion digital signal into analog form.
After a brief theoretical excursion, it's time to look at the internal equipment of the amplifier. We will start, as the people say, "from the stove." High quality amplifier performance is impossible without a powerful and stable power supply. So in NAD M 2, three independent power supplies are used, for the left and right channel, as well as for the control circuits. Each power supply uses a separate toroidal transformer to minimize magnetic pickup as well as eliminate transient cross-talk. Separately, it should be noted that the powerful output circuits of each amplifier channel, together with the transformers, are placed on separate printed circuit boards... Separate massive radiators cool the output transistors of the amplifiers of the right and left channels, so that their mutual heating, causing thermal drift of characteristics, is completely excluded. 
The digital amplifier was made possible by the use of Digital Feedback technology. This is a proprietary development of the companyZetex Diodes with which NAD collaborated on adapting this idea for use inNAD M2. Zetex Diodes specialists named their development "Amplifier with Direct Digital Feedback" ( Direct Digita l Feedback Amplifier DDFA).
Digital feedback, like conventional analog feedback (OC), minimizes signal distortion. Let me remind you briefly how the well-known analog OS circuit works. In it, the reduced value of the output signal in antiphase is fed to the input stage. By adjusting the amplitude of this signal, the level of nonlinear distortion is minimized.
But when we have a digital signal, there are many problems in the way of this approach. The main one is the time delay in the passage of the signal through the circuits, because even an error in time of 1 nanosecond can lead to significant distortions of the output signal. Innovative idea Zetex Diodes is that the real PWM output signal of a high level (at the output of the transistor) is compared with a reference PWM signal of a low level. The source of such a signal is a precision clock generator. The resulting error signal is digitized using a 35-bit DAC with a sampling rate of 108 MHz. Such DAC parameters allow minimizing not only the errors arising from the timing mismatch of signals, but also minimizing other potential sources of distortion.
The output stage of the amplifier is made using high quality field ( FET ) transistors. The output characteristics of the device correspond to modern requirements. And most importantly, the output power of the amplifier does not depend on the connected load, it does not matter if you use speakers with an impedance of 8 or 4 Ohms, RMS the power of the amplifier will be 250 watts (peak power up to 500 watts) per channel. Well, in terms of the level of nonlinear distortion, signal-to-noise ratio, as well as channel separation NAD M 2 can give a serious head start to any analog "colleague".
Using proprietary technology Digital power drive specially redesigned for use in a digital amplifier allowed the developers to get a good headroom. To prevent clipping of signal peaks at ultra-high power, the device uses a digital form of technology Soft Clipping.
The switching capabilities of the device are also extensive. It has five digital inputs. Among which are two optical, two coaxial and AES / EBU ... If you need to work with an analog signal, pairs are at your service XLR and RCA , the input stage is balanced. Of course, in this case, the analog signal is first digitized by a precision ADC and then amplified by a digital stage.
The developers have not forgotten about the corporate ideology. CI friendly, NAD M 2 is equipped with the necessary ports for automation control: trigger connection, IR input and computer interface RS -232.
Expertise.

Before moving on to describing the listening results, I want to tell you about the test system. As a source sound signal high quality CD-player NADM5 , the signal from which was fed in digital form via a coaxial cable to an amplifier NAD M 2. Evaluated the sound of the amplifier using an exclusive speaker systemKEFReference 203/2 ... A digital coaxial cable was used to connect the player and amplifier The chord company Codac, the acoustics were connected to the amplifier using a top-end speaker cable The chord company Solstice.
We have not forgotten about the high-quality power supply of our system. To connect the supply voltage, noise-immune electrical cables were used. Wire world Electra 5.2 ... The room itself has been acoustically processed; sound-absorbing plates are clearly visible in the picture. Look photos of the test system can be found in a special section of our photo gallery.
So, the first thing I noticed right after turning on the kit was silence. Do not be surprised, it may seem strange to someone, but the amplifier does not make noise at all, unlike analog devices, even at maximum volume. Thus, it is possible to understand whether the device is on or off only by looking at the display. 
The first song I listened to wasToccata and Fugue in D minor J.S.Bach from the demo disc KEFReference... This highly acclaimed piece is characterized by very deep bass at the beginning. And I will say right away that I did not hear the deepest bass that can be felt with the whole body. Then I will return to the topic of bass, but for now I will describe to you my impressions of the first listening. Before testing, I was warned that the sound of this amplifier is a little unusual, and differs from traditional analog sound. Honestly, I did not feel anything unusual in the nature of the sound, on the contrary, I heard a clear and juicy sound. The amplifier did an excellent job of conveying the volume of the soundstage, and it seemed to me that I was in about the third row of a concert hall. I would also like to note that the device conveys the dynamics of the piece with the same quality almost regardless of the volume level. The panorama created by the unit is much wider than the distance between the speakers. In my opinion, the main merit of the system is that even on this very difficult piece, I felt an almost one hundred percent effect of being in a concert hall. At the same time, the amplifier even has a certain academic sound.
As the next material, I chose an album of four concerts by JS Bach performed by the Hermitage Chamber Orchestra in a transcription by Alexei Utkin, released by the company Caro mitis ... I don't think I should be talking about the highest quality of this disc here.
I decided to start with track number 3 Concerto in A major for oboe d "cupid, strings and basso continuo (BWV 1055) - AllegroMaNonTanto. The sound of the recording delighted the ear with the breadth of the soundstage and impeccable authenticity. On this song, I liked almost everything, even the bass level. As in the first test NAD M 2 created a surround sound field and, what is most pleasant, the effect of being in a concert hall was preserved.
Then I complicated the task and set track number 5 Concerto in C minor for violin, oboe, strings and basso continuo (BWV 1060) - Adagio. And here the amplifier did not disappoint. Everything was at its best, the sound of the violins pleased with its airiness and authenticity. True, it is possible that lovers of soft sound will find the amplifier's performing style quite tough. The thing is that the sound produced by the device is distinguished by its fast attack and drive, but perhaps this is the very features of digital sound. After all, there are no analog circuits capable of "tightening" the front of the sound signal, about the impulse nature of which I have already written many times.
I tried it in tandem with pop music. And now we need to go back to the topic of the bass part of the spectrum. Incendiary Latin rhythms conquered me with a deep and energetic bass. At the same time, the bass could even be felt by the body. In my opinion, the device easily copes with bass with a fast attack, but the slow organ bass, as it seemed to me, sounded restrained, albeit with good detail.
Then I listened to compositions of electronic music, and there was complete harmony. True, one small drawback was noticed (or an advantage, on the other hand), having an uncompromising character of sound, the device is able to easily expose technical flaws in mixing. But this is precisely the very high fidelity of reproduction. Show all nothing, without hiding, is this what fans of pure sound strive for? 
I was simply captivated by the way the novelty reproduces jazz compositions. The whole room was filled with rich and clear sound, the amplifier reproduced even complex vocal parts with filigree precision. There were no noticeable flaws, not to mention the uncontrolled movement of instruments across the stage. The vocalist's voice was clear, rich, and airy, the sound of the sibilants was flawless. The only thing that can be a little blamed for the amplifier-acoustics bundle is the very slight harshness of the sound that I wrote about above.
And at the end of the test, I decided to listen to how NAD M 2 will cope with chanson, there is no need to "throw stones at me", I believe that this is the same musical genre as the others. By the way, its place is clearly indicated in the same saying: "Russian, folk, thieves, round dance". In general, this is completely normal test material. For listening was taken CD Tatiana Kabanova "From the classics of chanson and not only ..." I chose this particular performer for her very effective voice a bit like Edith Piaf and an unusual manner of performance. On this material, the character of the sound of the system was a little different, I had a feeling more like being in a recording studio opposite the vocalist. To be honest, this is the first time I have heard such a very interesting effect outside the studio. And believe me, it's worth a lot.
Let's summarize.
So, it's safe to say that the figure came in High end for a long time and seriously. New digital amplifier NAD M 2 is able to squeeze out traditional analog systems in this market, and not only in terms of sound quality, but also in terms of price.
You can, of course, slightly reproach the device for the overly academic nature of the sound, but it was not for nothing that I noticed that this is the very high fidelity of sound that any self-respecting audiophile strives for. And as for the noted slight rigidity of the sound, then she has many fans.
In my opinion, the main advantages of the novelty are the pronounced effect of being present in the concert hall and the high fidelity of the sound.
Amplifier Specifications NADM2 :
Output power - 2 x 250 W ( continuous power) at 8 and 4 Ohms
Dynamic power IHF -> 500W
OIG -<0.004% на диапазоне 20 Гц – 20 кГц от 500 мВт до 250 Вт
Signal ratio/ noise - 126 dB / 90 dB ( at full power/ for 1 W)
Dynamic range - 120 dB
Residual noise - 40μV
Dumping factor -> 2000 at 50 Hz + 0 / -0.5 dB at 20 Hz - 20 kHz, -3 dB> 85 kHz
More recently, the two-channel high-end amplifier was considered the last analog bastion to resist the onslaught of digital sound. Attempts by some brands to create a flagship component that work in class D met with strong opposition from audiophiles. The very term "digital amplifier" offended the ears of high-quality sound lovers. However, with the success of NAD's M32, the top-of-the-line Master Series, things have changed dramatically.
This year the NAD trademark is 45 years old. It was formed in 1972 and has long relied on traditional audiophile values. All the more expensive are her efforts, thanks to which a serious reassessment of values began among audiophiles. Indeed, is it worth, like a drowning man drowning in a straw, clinging to an analog amplifying path, if the vast majority of musical information comes to us in digital form?
Gentleman's set
Even before you can remove the case made of high-quality packaging material from the amplifier, you feel the solidity of the design: with a relatively low height (133 mm), the weight of the device is no less than 18.5 kg. Front and side panels made of aluminum - a non-magnetic material that prevents the propagation of electrical noise.
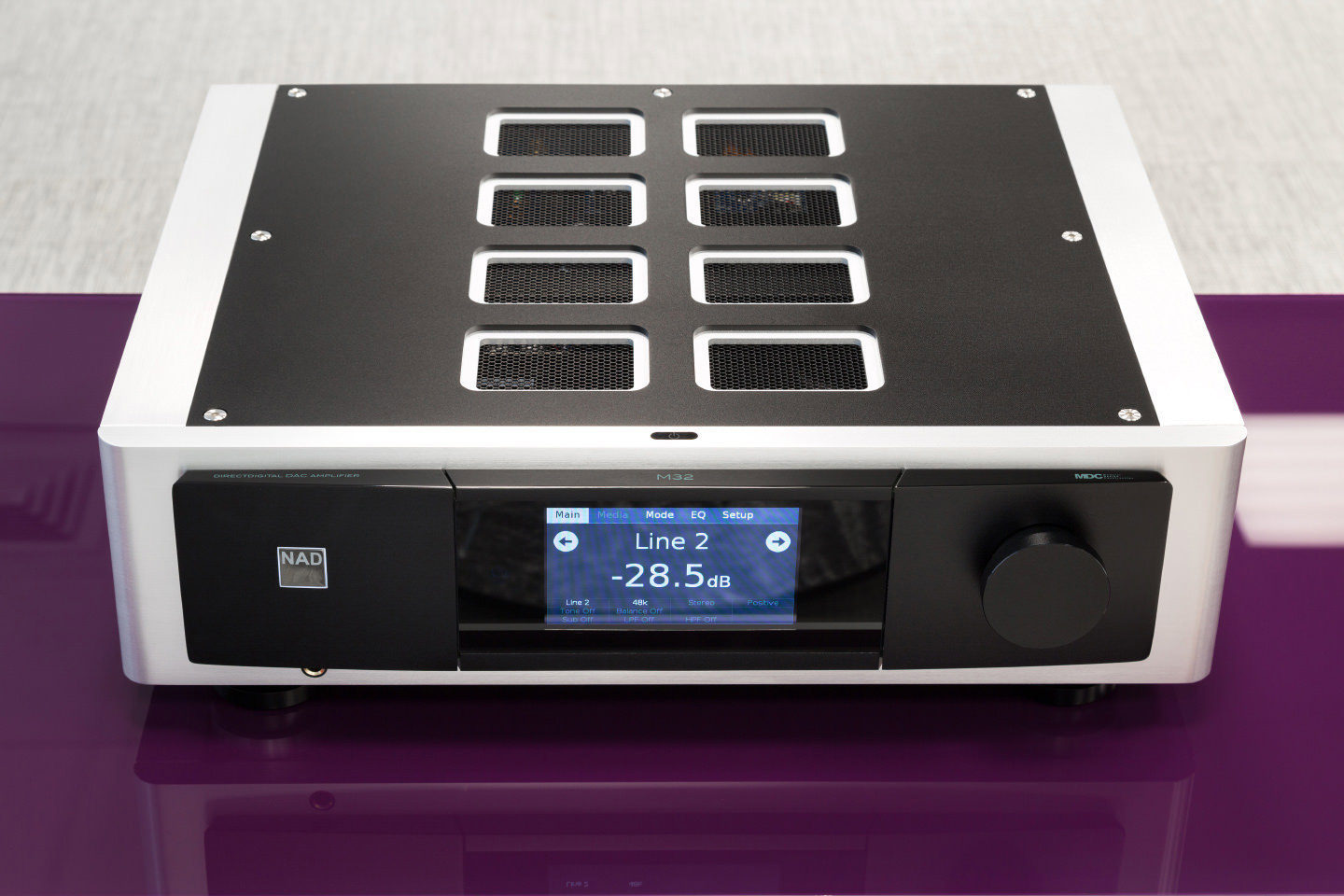 The central place on the front of the amplifier is occupied by a touchscreen display, on which all the necessary information is indicated - from the name of the input and the volume level to the option of equalization
The central place on the front of the amplifier is occupied by a touchscreen display, on which all the necessary information is indicated - from the name of the input and the volume level to the option of equalization The designers did everything to make the facade look extremely neat, in particular, the power button is placed in the middle of its upper edge. The black cover slightly protrudes from the front panel, visually increasing the size of the colored touch display that displays all the information the user needs. On the left under the cover there is a 6.3 mm headphone output, on the right is the volume control knob, made in the form of a truncated cylinder - it is very ergonomic. By the way, I note that the control accuracy is 0.5 dB - a fairly high indicator for a digital amplifier.
 Accessories include boots to protect the rack from scratches caused by the spiked amplifier legs
Accessories include boots to protect the rack from scratches caused by the spiked amplifier legs To ensure mechanical decoupling from the surface on which the amplifier will be installed, the legs are made in the form of thorns, and in order not to scratch it, the so-called. shoes made of elastic material.
However, the most "tasty" accessory is the instruction. It is presented in in electronic format, on a flash card in a case made of genuine leather (neither give nor take - a holster, you look at it and you want to compose a slogan, for example: "a manual is an audiophile's weapon").
Suit for growth
The rear equipment exceeds the expectations of the most demanding consumer. In addition to two pairs of high-quality bi-wiring screw terminals, there are three analog stereo inputs - two line-level and one for the MM cartridge of a turntable. There is also a preamplifier output, which, if necessary, can be used to feed a low frequency signal for a pair. active subwoofers.
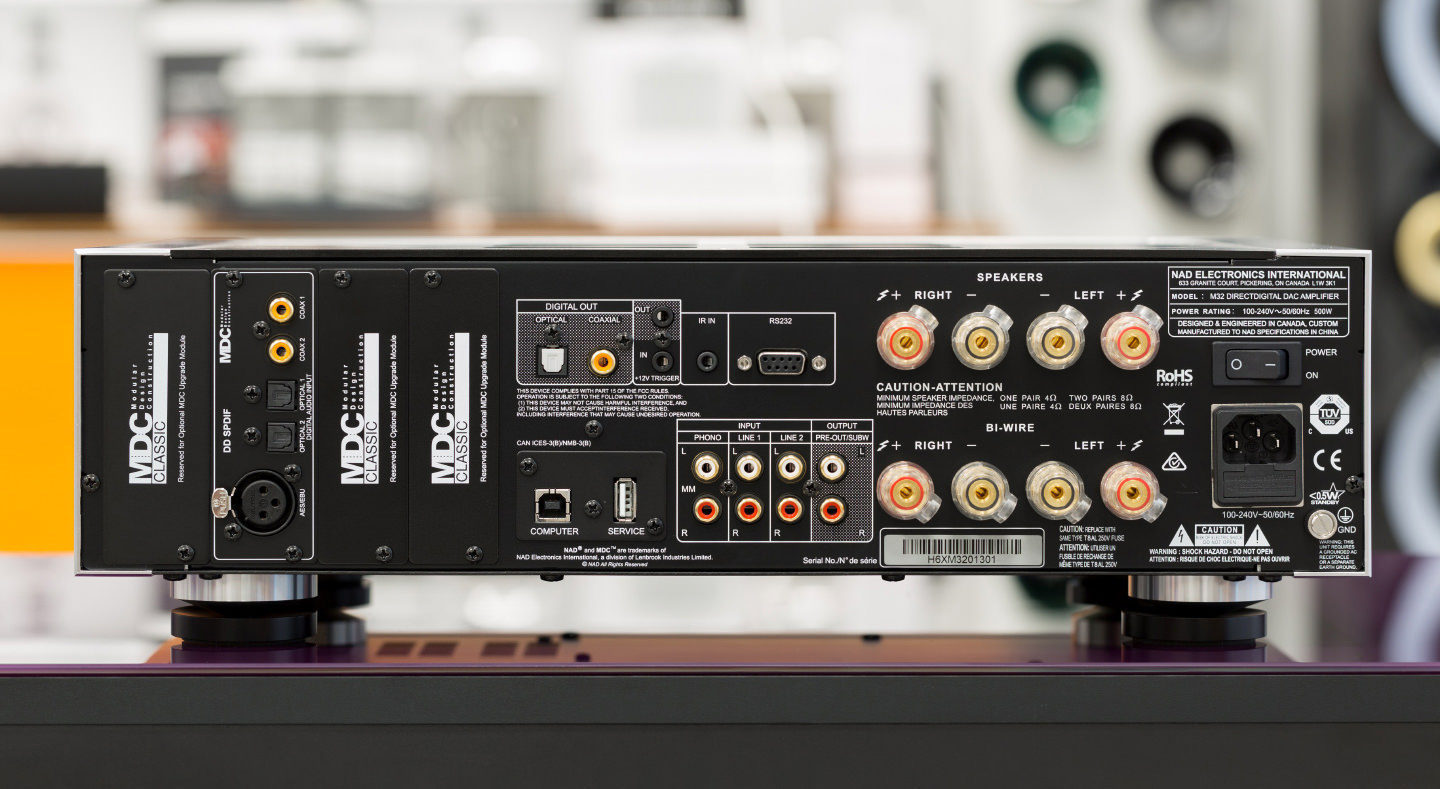 Rear panel of the amplifier. Pay attention to the high quality speaker terminals and USB ports- computer (type B) and service
Rear panel of the amplifier. Pay attention to the high quality speaker terminals and USB ports- computer (type B) and service Of course, the amplifier is equipped with a full range of digital ports: two optical and coaxial outputs and one corresponding output are provided (as you can see, the M 32 can also be used as a high-quality ADC for digitizing, say, rare gramophone records or exclusive tape recordings). There is a balanced AES / EBU input - the developers recommend using it to transmit an audio stream with a sampling rate of 176 kHz or 192 kHz from a SACD / CD player. A similar signal up to 24/96 can be received from a PC or Mac computer via the USB B port (next to it is the USB A socket, but it is used only for service). Through the RS-232 port, the amplifier can be connected to a multi-room control system (AMX or Crestron), and by means of a 12V relay signal (corresponding input and output are provided), the amplifier can be used to control the on / off of another device or, conversely, turn on / off the amplifier when it is turned on / turning off the external component.
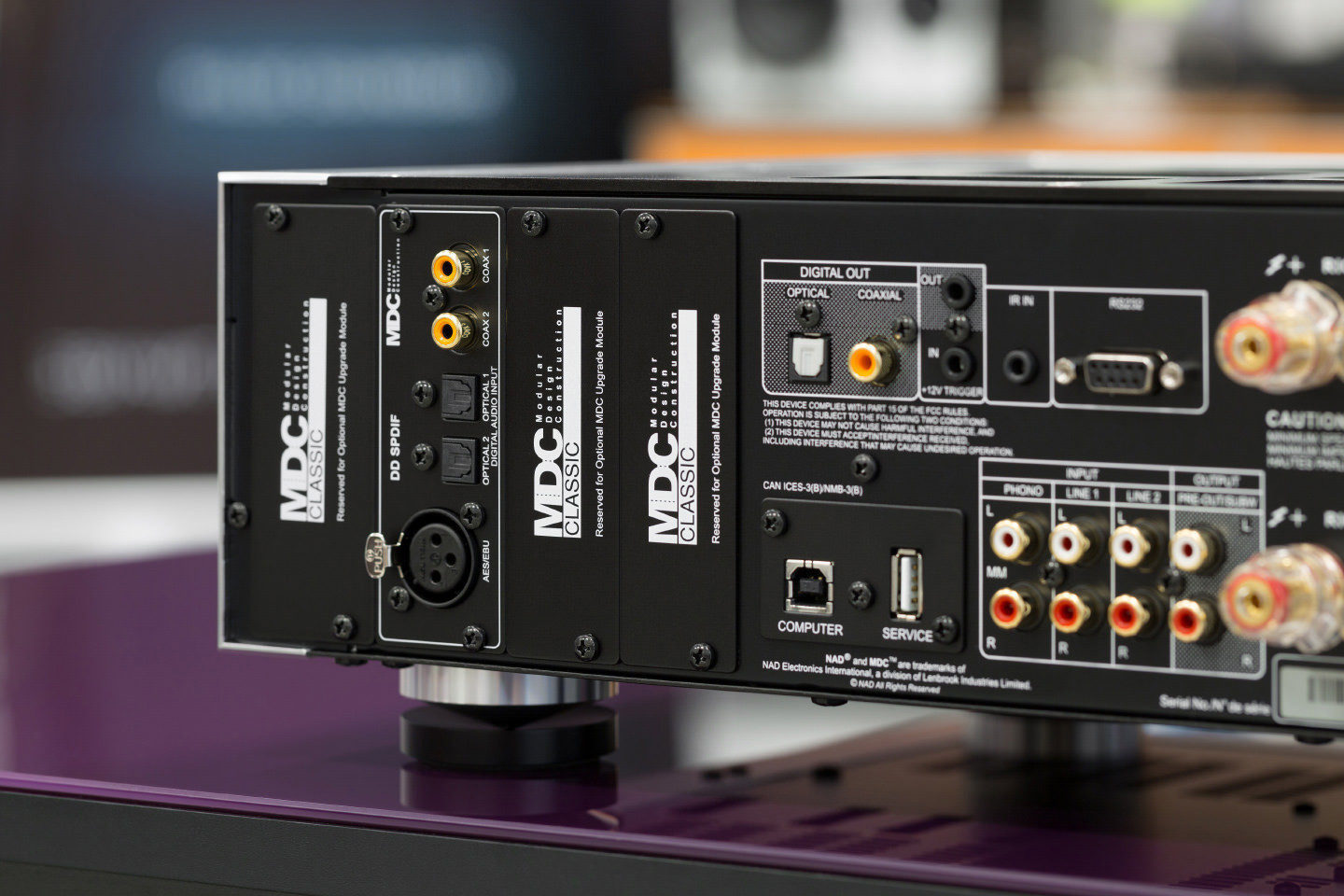 This is how the footprints for three additional optional modules look like.
This is how the footprints for three additional optional modules look like. “And what exceeds my expectations? - the above-mentioned demanding buyer will ask. "Most of the M32's competitors can boast of such a commutation set." In response, I will draw the attention of my opponent to one discreet, but very important feature of the organization of the rear panel of the amplifier. The digital inputs are a separate module: it is easy to remove and replace with another. Moreover, there are seats for three more similar modules nearby.
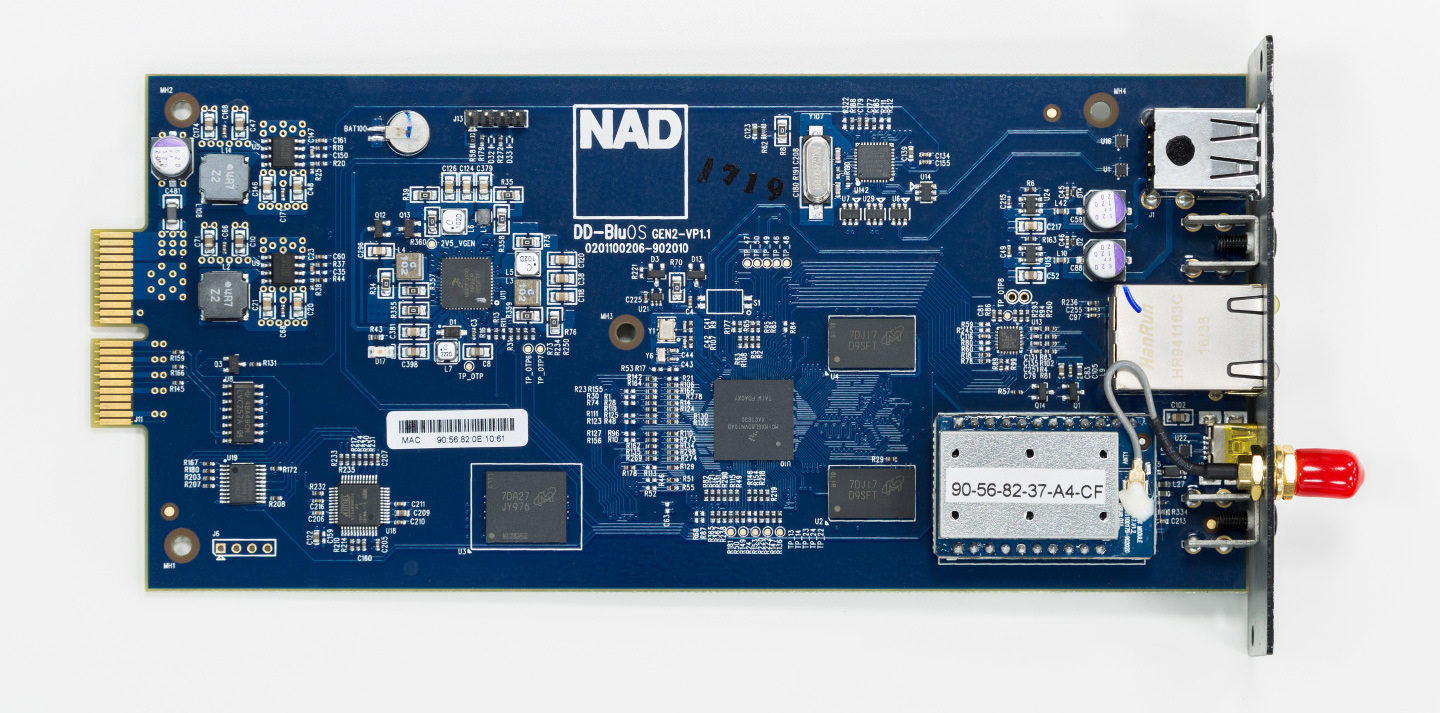 The optional MDC BluOS board in all its on-chip glory
The optional MDC BluOS board in all its on-chip glory In particular, you can install a DD AP 1 module with a balanced input, as well as DD-HDM 1 (three inputs and an HDMI output) and organize a home theater based on the M32, receiving PCM 2.0 sound from a Blu-ray / DVD player. Or equip the amplifier with an MDC BluOS module for streaming internet services via a dedicated software BluOS (with support for MQA, AAC, Ogg, MP3 and even Bluetooth aptX). 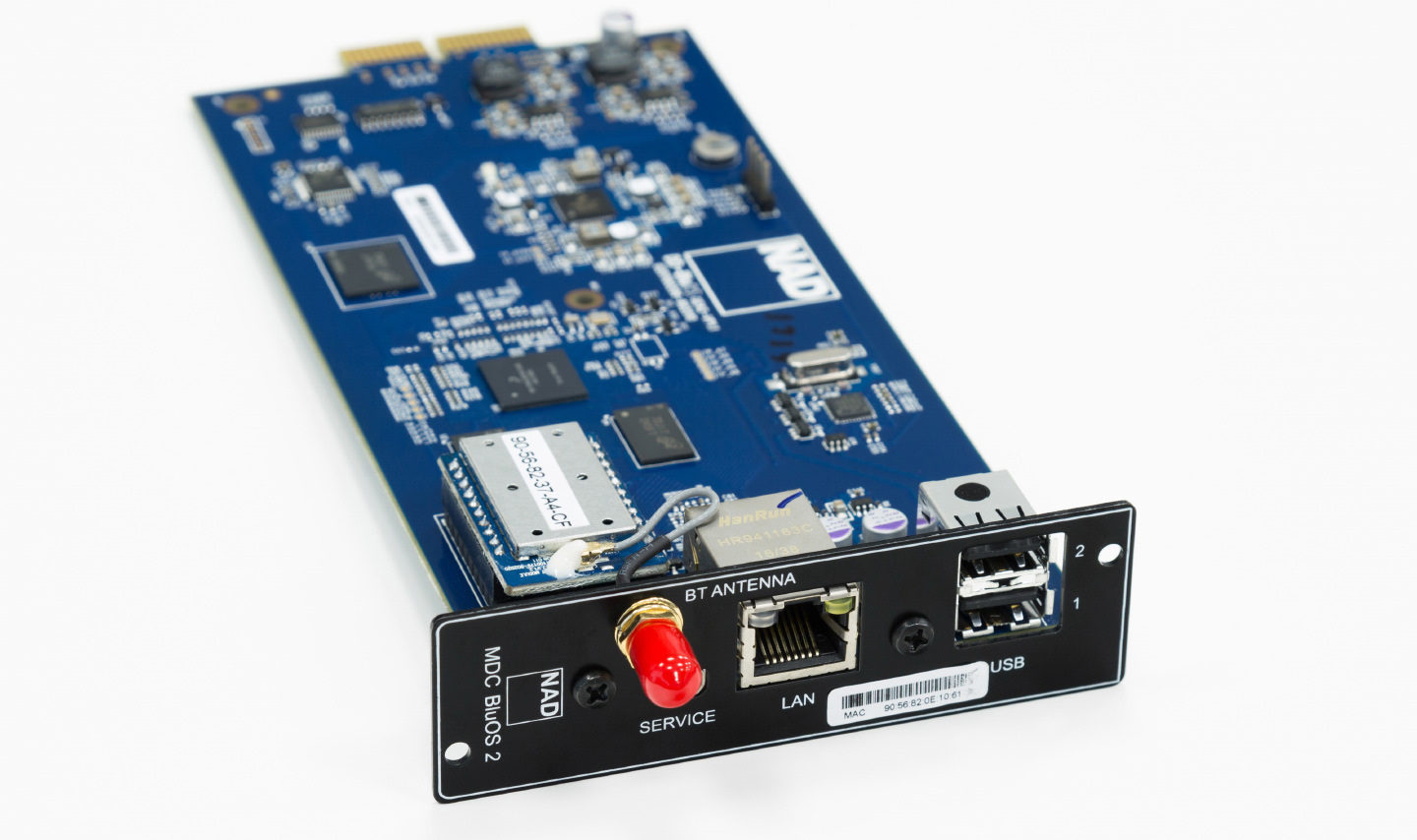
All this is part of a proprietary technology (or, if you prefer, a strategy) called MDC (Modular Design Construction) and designed to protect the amplifier from obsolescence, and due to the rapid development of digital formats, it can come very quickly.
Features of circuitry
NAD's drive to move away from analog amplification is driven not only by a revolution in the world of audio media, but also by the possibilities the digital amplifier is opening up. First of all, they relate to matching with loudspeakers (as you know, their impedance depends on the frequency of the reproduced signal, and can be reduced to 1 Ohm, which is an unbearable load for a device operating in class A / A – B).
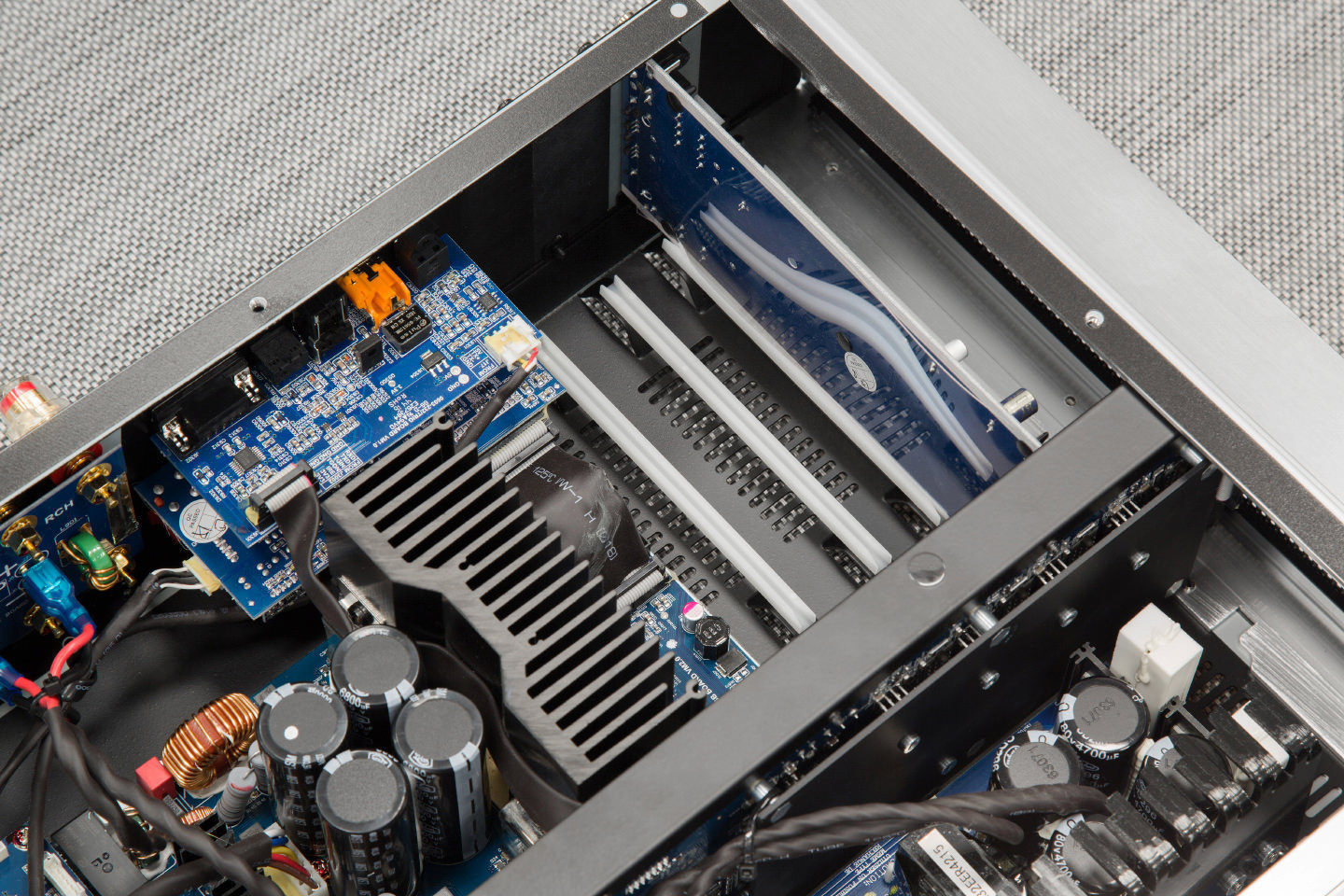
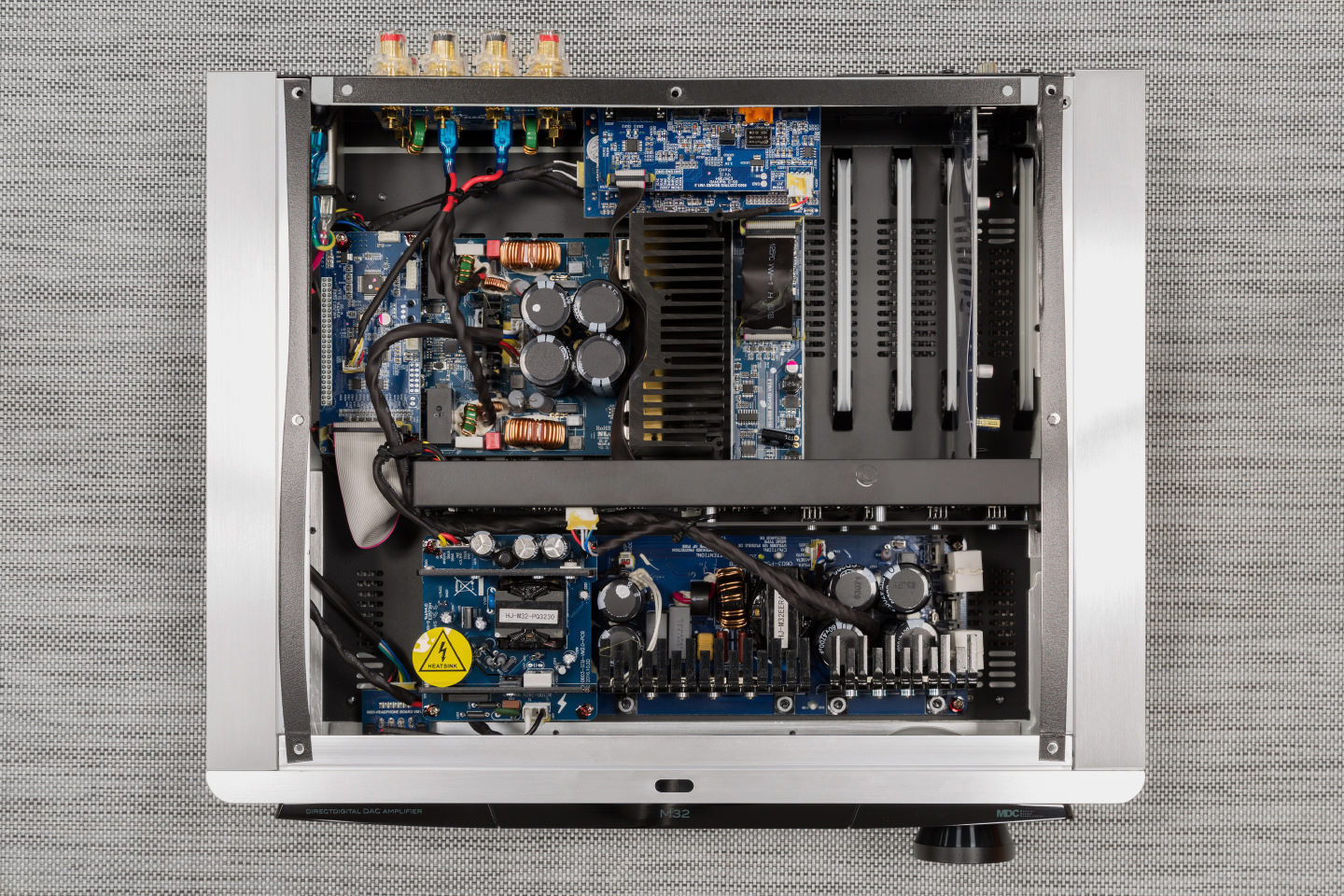 Under the hood of the amplifier - not an inch of free space
Under the hood of the amplifier - not an inch of free space NAD engineers have been working on the creation of an amplifier that is practically insensitive to changes in speaker impedance for more than five years. As a result, the option of digital amplification with feedback was chosen, based on the developments of the English company Diodes Zetex (hence the name of the amplification class - Z).
 The chassis is divided into compartments, which prevents the propagation of interference and interference and increases the mechanical rigidity of the structure
The chassis is divided into compartments, which prevents the propagation of interference and interference and increases the mechanical rigidity of the structure The pulse code modulation of the input PCM signal is converted to pulse width modulation; the corresponding signal and controls the powerful field-effect transistors operating in the key mode (DDFA technology - Direct Digital Feedback Amplifier, "direct digital amplification with feedback"). Feedback is needed just to take into account the load impedance: a special processor measures it more than 100 million times per second (!) And makes the appropriate correction. As a result, the damping factor of the amplifier exceeds 2000 units, which allows maintaining the output signal level with an accuracy of 0.5 dB when the speaker impedance changes within 1–8 Ohm.
Functional set
In terms of audio settings, the M 32 comes close to the AV receiver. In particular, when outputting a subwoofer signal to the PRE OUT connectors, you can change the frequency of the transmission of the sound relay from the speakers to the subwoofer (40-200 Hz) and the signal level (–12 dB - 0 dB), and when a pair of woofers is connected, the mode of their operation ( stereo or mono).
Of course, there are controls for balance and LF / HF timbres, as well as a special filter designed to smooth out unevenness in the reproduction of high frequencies caused by the impedance of specific speakers (when setting up, the passport value of their impedance is set).
 Flash card with user manual and holster for it
Flash card with user manual and holster for it Any input can be named. You can also disable general regulator volume or ( useful function if the M32 works as part of a multichannel audio system, the sound level of which is regulated through an AV processor) "fix" the signal level from any of the line inputs. Since these inputs are an analog signal, it must be digitized before amplification. But in what format? It is up to the user to decide: he has three sampling rates to choose from - 48, 96 and 192 kHz.
 Aluminum remote remote control is a good foot long and weighs at least a pound
Aluminum remote remote control is a good foot long and weighs at least a pound The mode is provided automatic shutdown at 15 minutes idle time. If you have multiple NAD components in your system, you can make them respond only to commands from your “own” remote control. Conversely, in the presence of components third party manufacturer the standard remote control can be taught to operate them (there can be up to seven such devices).
Sound
For testing, the amplifier was connected to a ProAC Carbon Pro8 three-way floorstanding speaker with ribbon tweeter. They have a fairly high sensitivity (91 dB), but a low (4 Ohm) impedance, which in the light of the above seemed very important to me. A SIM Audio MOON Neo 260D CD-player was used as a source.

The first thing you pay attention to when listening, or rather, before starting it, is the unusually low level of its own noise. Only when you come close to the loudspeakers, you can catch the slightest rustle, indicating that the amplifier is on.
First, it was decided to check how the M 32 handles the analog signal - the line output of the player was connected to the Line 1 input of the amplifier. On test material of all times and peoples - the album "The Dark Side of the Moon" by Pink Floyd (FLAC 24/96) - the M32 impressed with its ability to create a three-dimensional soundstage. Rather, he was amazed at the confidence with which he tamed the floorboards. The recording was two-channel, but I recalled that once it was released on vinyl in a quadraphonic version: the M32 created a full sense of depth. It seemed that David Gilmore and his comrades came to visit me, settled down at ease in the listening room and played a song there.
 The volume control knob is made in the form of a truncated cylinder
The volume control knob is made in the form of a truncated cylinder Then the amplifier and turntable were connected via a balanced digital AES / EBU bus. Something has changed in the sound, but almost imperceptibly (a fact that eloquently testifies to the high quality of the M 32 analog-to-digital converter). I cannot definitely recommend such a connection - it all depends on the tastes and preferences of the owner - however, I strongly advise you to conduct such an experiment.
Worthy of the highest praise and "omnivorous" amplifier: jazz, rock, electronic music and vocals were reproduced with the same (almost surgical) accuracy. The sound is extremely balanced, while the self-confidence of the amplifier was clearly felt - it squeezed out every last nuance from the recording, invariably creating the impression that it still had two dozen decibels of dynamic range and octave in bass and treble in stock. I am quite sure that it will not be difficult for him to swing any acoustics, even the notorious magnesian planars, which are very difficult to "train".
 In the very center of the upper edge of the amplifier there is a touch-sensitive power button
In the very center of the upper edge of the amplifier there is a touch-sensitive power button I regretted not grabbing more assertive material for testing (you must admit that potential buyers are unlikely to be fans of, say, Blind Guardian). However, the fantasy overture “Romeo and Juliet” by P.I. Tchaikovsky. It ends with a powerful crescendo, the high-quality reproduction of which requires all efforts from the audio system, however, this did not confuse the M 32: it again demonstrated a virtuoso ability to work out signals with steep edges. If this is the digital future of amplification, then let it quickly become the present. True and complete.
Advantages: ability to work with any acoustics, modular design, the presence of a regular Phono-input
Disadvantages: touch-sensitive power button reacts to touch for a long time
Price: 330,000 rubles
Passport data
Output power: 80 W (20 Hz - 20 kHz, THD 0.03%)
Signal to noise ratio: more than 91 dB (1 W, 8 ohms)
Damping factor: more than 1000
Inputs: 2 stereo analog, 1 phono, 2 optical, 2 coaxial digital
Outputs: 1 stereo, 2 per subwoofer, 1 headphone 6,3 mm
Interfaces: USB B + A (service), RS-232C +, IR sensor, 12V relay signal input / output
Power consumption: 400 watts. (Standby 0.5W)
Dimensions 435x133x396 mm
4WD RC Monster Truck Off-Road Vehicle 2.4G Remote Control Buggy Crawler Car Blue| $17.98 End Date: Wednesday Dec-6-2017 19:29:36 PST Buy It Now for only: $ 17.98 | |
3800 rub
Vase "Thistle". Porcelain, underglaze and overglaze painting, gilding. LFZ. USSR, second half of the twentieth century
Vase "Thistle". Porcelain, underglaze and overglaze painting, gilding. LFZ. USSR, second half of the twentieth century.
The sculptor is S. E. Yakovleva. Artist - L.K.Blak.
Height: 31.5 cm.
Body diameter: 12.5 cm.
Based on blue
14167 rub
Delilah necklace. Glass, white genuine leather. Cristalida, Argentina
5700 rub

St. Petersburg, 1861. Printing house of the Imperial Academy of Sciences.
Owner's binding. With the attachment of a portrait of P. S. Savelyev and a photograph from his handwriting. The preservation is good.
From the preface: "The Imperial Archaeological Society, shortly after the death of founding member Pavel Stepanovich Savelyev in May 1859, turned to his friend and university colleague Vasily Vasilyevich Grigoriev, a corresponding member of his, with a request to compile a biography of Pavel Stepanovich, who rendered so many services Society ... "
Pavel Stepanovich Savelyev (1814-1859) - Russian archaeologist, orientalist-Arabist, numismatist. The main merit of Savelyev lies in a number of discoveries in the Golden Horde numismatics, in a new definition of the topography of coin hoards in Russia and in the popularization of numismatic and archaeological information about the East. He advocated the preservation of ancient monuments.
23399 rub

St. Petersburg, 1900. Published by A.F. Marx.
New-made owner's binding with gold stamping. Patterned bleed. The preservation is good.
The text of the poem by N.V. Gogol's WALKING CHICHIKOV OR DEAD SOUL according to the latest edition of Academician N.S. Tikhonravov, with a portrait of N.V. Gogol engraved on steel, 10 heliogravures and 355 illustrations by artists: V.A.Andreev, A.F. Afanasyev, N.N. Bazhin, V. I. Bystrenin, M. M. Dalkevich, F.S. Kozachinsky, I. K. Mankovsky, N. V. Pirogova, E. P. Samokish-Sudkovskaya, S. S. Solomko and N. N. . Khokhryakova. Letters and vignettes by N.S. Samokish.
The publication of the first volume of the poem DEAD SOULS (the title was changed by the censor: CHICHIKOV'S APPEALS, OR DEAD SOULS) became a significant event not only in literary but also in public life in Russia. Some saw in this essay only an intention to offend a Russian person, while others admitted that it was a great work.
The second volume of the poem DEAD SOULS, on which Gogol worked long and hard and which undermined his strength, came out after the death of the writer. These are the surviving chapters of the manuscripts that Gogol devoted to the fire. The early and later editions of the second volume of the poem, printed in all editions, make it possible to outline the author's intention in general terms, but the secret of the burned manuscript will forever remain a mystery.
The publication is not subject to export outside Russian Federation.
126900 rub

Lifetime edition. Moscow, 1922. "Rosevnik" publishing house. Typographic cover. The preservation is good. According to one of the ancient models, everything in the world consists of the elements: fire, water, earth - and is either in the state of gas, or liquid, or solid. But what about the man? His soul? His mind? As a natural being, our great poet A.S. Pushkin believes, these states are also inherent in him. And it is they who determine the life of a person. Pushkin brilliantly outlined these states in the manifestation of human passions, in the birth and death of a person. And if, reading Pushkin, you do not see his images, then you understand him in the same way as a Russian person - Belarusian or Ukrainian. This book by the Russian literary critic Mikhail Osipovich Gershenzon will help you understand Pushkin.
7590 rub
A decanter with a "Swan" figurine inside. Glass, cast technique, painting. USSR, 60s of XX century
A decanter with a "Swan" figurine inside. Glass, cast technique, painting. USSR, 60s of the XX century.
Height (with plug): 26 cm.
Body diameter: 10 cm.
The preservation is good.
Similar decanters were widespread in Russia from the beginning of the XIX
11667 rub

St. Petersburg, 1890 - 1907 Brockhaus-Efron edition. Illustrated edition with figures on separate sheets. Typographic bindings, gold-embossed leather spines. The preservation is good. In Russia, as you know, there have been repeated attempts to publish publications of this kind. In addition to the very venerable short editions of the reference explanatory dictionaries of Dal, Tol, Simonov, and others, there were also publications of large Encyclopedic Dictionaries: Plushar, very remarkable in content, but, unfortunately, stopped at "Af", then undertaken by Professor I.N. Berezin, the publication of the Russian Encyclopedic Dictionary, and others. The proposed edition of the Encyclopedic Dictionary was published by the large publishing company of F. Brockhaus (Leipzig), which has gained great popularity in Europe, in conjunction with the company of I. A. Efron (St. Petersburg). The Encyclopedic Dictionary is based on the famous German (XIIIth) edition of Brockhaus, Conversations Lexicon, with all its rich applications of both geographical maps and drawings. All articles concerning Russia, and they are given a wide space, are placed in the Dictionary completely independently, presenting extensive material. Initially, the encyclopedia contained mainly Russian translations of the articles of the Brockhaus encyclopedia with a small adaptation for the Russian reader. The first 8 volumes (up to the letter "B were published under general edition Professor I. E. Andreevsky. These volumes caused a lot of complaints about the quality of the translation, and the overall management of the publication also left much to be desired. A new period in the history of the encyclopedia began with the invitation to the editorial board of many prominent scientists and philosophers of that time: DI Mendeleev, Vl. S. Solovyov, S. A. Vengerov, A. N. Beketov, A. I. Voeikov and many others. From that moment on, the encyclopedia begins to replenish with original articles, and the main attention is paid to issues related to the history, culture and geography of Russia. Another feature of the encyclopedia is the free manner of presentation. Elements of fiction are found not only in biographical articles, many of which read like gripping stories, but also in scientific ones. In many respects, such looseness in the presentation of the material is also a consequence of the involvement of the most prominent scientists of that time in writing articles, because, as you know, only those who are freely oriented in this area can explain something most intelligibly. Moreover, at that time it was not customary to edit articles, "combing" them one size fits all, and the author's style remained intact. The edition came out in two versions - 41 main volumes and 2 additional (smaller part of the circulation), 82 basic and 4 additional half volumes. The first option is offered to the readers' attention. The publication is not subject to export outside the Russian Federation.
244900 rub

China (?), Second half of the 19th century. No publisher specified. Owner's binding. The preservation is good. In the entire history of world philosophy, there are few thinkers who could be put alongside Confucius. The legendary great Teacher, an indisputable authority for the Chinese philosophical tradition, he has long stepped over its not at all narrow limits. The legacy of Confucius, if we discard the mass of dubious and frankly attributed to him texts, is very laconic. However, the philosophical system developed by the thinker and his students has been feeding Chinese and world culture for more than two millennia, regardless of political turns and historical changes. Your attention is invited to an album of engravings, which capture the plots of Confucius' parables and moments of the life of the legendary Teacher. Not subject to export outside the Russian Federation.
When we test amplifiers for car audio systems in our acoustic laboratory, we often mention their classes in the materials, they say, this one works in the economical class D, and that purely for audiophiles - in the Real AB class. And then I was recently asked a question: what kind of classes are these in general? Well, let's figure it out.
When choosing a suitable amplifier for an audio system in a store, pay attention to the class in which they work. Class AB can be called traditional, most amplifiers work in it. Recently, more and more class D amps, which are called digital, are becoming more common, although this is not entirely correct, and you will soon understand why. Which one to prefer? Which is better? As usual, there is no definite answer, as each has its own advantages and disadvantages. But first, a few words about what and how it generally happens inside.
WE SHALL TOKU
The basic elements of almost any amplifier are transistors. We will not go into the essence of the construction different schemes, especially since they are actually far from one, but we will single out the main thing - the very principle of operation. To do this, for a while, let's imagine the amplifier in the form of, well, let's say ... a water supply system. Unexpected, right? Nevertheless, the analogy is there, and you will see this now. Firstly, the amplifier has a power supply that converts the unipolar voltage of the on-board network ("plus" and "ground") into a bipolar one ("plus", "ground" and "minus"). We have already said why it is necessary when we considered So, in such a system, a bipolar power supply will be nothing more than two pumps (the pump on the "+" side will, as it were, pump, and the pump on the "-" side will, as it were, pump out the current relative to the mass Our task is to let these flows through the load of the amplifier (the load is just the speaker connected to the amplifier). For this, of course, we need taps that will control these flows.
This is exactly the role of these taps and transistors play. They can open, letting a large stream pass through themselves, or close, reducing it. These "valves" are opposite to each other: when one starts to close, the other will open. Accordingly, the flow from the "pumps" will be directed through the load in one direction or the other. And it is the input signal that controls all this opening-closing.
AMPLIFIERS CLASS A. B, AB, H
But in fact, just opening and closing the transistor is still not enough, because we need the signal to be amplified without distortion, that is, so that the output signal exactly repeats the input signal in shape. This means that we need the transistors (these same taps) to open and close according to a strictly linear law, strictly proportional to the input signal.
But here's the bad luck, in fact, the transistor may not work this way in its entire range. For example, if the input signal is too small, then the transistor almost does not react to it, but when a certain level is reached, it opens abruptly. What kind of linearity is there? But beyond this moment, it reacts to a change in the control signal quite adequately, almost linearly. This means that in order for the distortion to be as small as possible, the transistor will have to be kept open all the time. This is called setting the bias of the transistor or choosing its operating point.
In this case, the amplifier is said to work in class A. This class of amplifiers is rightfully considered audiophile, since it provides very little signal distortion. But its main drawback is its high quiescent current. The quiescent current is the current that will flow through the transistors, even when there is no input signal (after all, we had to give the transistors some offset). Because of this, they get quite hot, and a significant part of the energy from the power supply goes into heat, and the efficiency of the amplifier is, at best, only about 20-30%.
But since car amplifiers are actually not made on one transistor, but are built on the so-called push-pull circuits, i.e. with 2 transistors, one tempting idea arises. What if you don't keep them open all the time? Let them both be closed in the absence of an input signal? Since the transistors are opposite to each other, it turns out that one of them will open when the signal is positive, and the other when the signal is negative. In other words, it turns out that the first will amplify the positive half-wave of the signal, and the other - the negative one, while under load these halves will add up safely. When the amplifier operates in this mode, it is said to be class B.
The solution is undoubtedly good, because a useless current does not flow through the transistors in such a circuit when there is no signal, which means that the efficiency of the amplifier is much higher. However, everything would be great, but the fact is that no matter how good and high-quality transistors we supply, they will still have nonlinearity at the very beginning of their opening. And this means that at the moment when one transistor just closes and the second just opens, a distortion in the form of a step will inevitably appear.
When the signal level is high, this step does not look very big, and if you don't find fault with it, then you can still not pay much attention to it. But at low signal levels, it will already be too noticeable. Therefore, class B in its pure form in car amplifiers not used due to high distortion.
So what is the best mode for an amplifier? In class A, there are small distortions, but the efficiency is also low, the lion's share of the power supply's power will go into heat (that's why amplifiers operating in this class heat up like irons). Class B will provide good efficiency, but the distortion will be such that it will not be necessary to talk about high reproduction quality. The compromise solution is mixed mode, where the transistors are provided with only a small offset, much less than in pure class A, but already sufficient to avoid a noticeable step in the output signal. At the same time, they say so - the amplifier works in class AB.
Choosing the operating point of the transistors (well, or in other words, choosing how much the transistors will be slightly open in the rest mode, that is, in the absence of an input signal), you can make the class AB amplifier closer to class A or to B. For example, in the first case, the effect is most noticeable, that until a certain power is reached, the amplifier operates in class A, and at high levels as if automatically goes into class AB - a solution that is quite often used in high-end amplifiers (sometimes in the descriptions for such amplifiers you can find the designation of their class as Real AB).
In fairness, it should be noted that classes A, B and AB are not the only ones. There are others that can be called derivatives of them, they are attempts to combine the economy of the AB-class with the quality of the A-class. For example, class A + is a symbiosis of class B and A-class amplifiers (the output of the first is the midpoint for the second). Or class Super A (Non Switching) - in them a special circuit does not allow the transistors to completely switch off (after all, the main distortions, as you already know, are precisely due to nonlinearity at the very initial moment of opening the transistors - "taps"). And class G amplifiers in general, they are two amplification stages, each operating from its own power source of different voltages (a cascade operates at low power, powered by a source with a low voltage, and at the peaks a second one is connected to it, powered by a source with a high voltage). complex circuits, which are used less and less in home appliances, and even in car amplifiers it is, to put it mildly, completely exotic.
But class H amplifiers can be safely called purely automotive. In this class, amplifiers are made built into the head unit. It is clear that they do not have any complex power supplies that convert onboard 12 Volts to bipolar nutrition with a high voltage (however, the amplifier built into the GU is still powered by a bipolar voltage, it is just that Upit / 2 is taken as the midpoint for it, that is, relatively speaking, 6 Volts), so the power of such amplifiers is low. Class H is an attempt to to some extent neutralize the main disadvantage of low-power amplifiers - sound jamming. So how does it work?
In fact, a Class H amplifier is essentially the same as a conventional Class AB amplifier. Only it has a so-called supply voltage doubling circuit, the main element of which is a capacitor that accumulates charge when the input signal is not very large. Well, since a real music signal is not a sine for you, on which power is measured according to the standard, then it is characterized by short-term peaks. So, just at the moments of such peaks, this very capacitor is added in series to the supply voltage by a special circuit, and it doubles, as it were, for a short time, helping the amplifier to reproduce these peaks with less distortion. This, in fact, does not really affect the power of the amplifier, measured as standard on a sinusoidal signal, but subjectively it sounds better at mid and high frequencies.
BY THE WAY
The class of the amplifier in the first approximation can be recognized by the nature of the dependence of the THD on the power. Look, at low signal levels, class A provides the smallest distortion. But class B, due to the "step" in the signal at low levels, will certainly have increased distortions (the so-called problem of the first watt). Class AB is somewhere in between.
CLASS D AMPLIFIERS
Classes A, B, AB and their other derivatives are all traditional classes of analog amplifiers, their construction principles are similar, except that the operating modes of the transistors are different, and some gadgets are added. But there are also amplifiers that are initially built somewhat differently. These are class D pulse amplifiers (by the way, they are sometimes called digital, although in fact, technically this is not very correct, nothing is translated into digital form there). Let's take a rough look at how a Class D amplifier works.
The first step is to convert an analog input signal (that is, a conventional continuous signal with varying amplitude) to a pulsed signal (a signal with constant amplitude but discontinuous). Moreover, the durations of the following pulses and pauses between them will be different, but most importantly, they will be in strict dependence on the input signal. For example, the higher the amplitude of the input signal - the pulses are longer, the lower the amplitude - the pulses are shorter. This is called Pulse Width Modulation (PWM).
Now received pulse signal need to be amplified, and this is done in the same way as in conventional amplifiers. And then the question may arise: why bother converting the signal into a pulse one, if it still has to be amplified, as in a conventional amplifier? It turns out that it makes sense. The fact is that the transistors in this case will work in a completely different way - in the key mode. That is, they will be either completely open or completely closed, with no intermediate options. But for such work, firstly, there is no need to select transistors with a linear I - V characteristic and try to get to the linear section of this characteristic. Secondly (and this is, in fact, a consequence of the first), the efficiency of such amplifiers can easily come close to the ideal of 100%. But this is an indicator that is unattainable for conventional amplifiers in principle. So we amplify the impulse signal, and we are glad how easy it is for us.
However, it is, of course, too early to send such an amplified pulse signal to acoustic systems (how, let me ask, will the diffuser dance to such a signal?). To do this, you need to convert it to a conventional, analog form. This can be done using an inductor and a capacitor, which together will form an LC filter. Having passed our pulse PWM signal through them, at the output we will receive an amplified signal that repeats the input signal in its shape.
The main advantage of D-class amplifiers is their high efficiency. However, there is also a serious drawback - frequency range amplifier is most often severely limited from above. It is this for a long time that was the reason for the use of this technology only in monoblock bass, designed exclusively for subwoofer use. However, with its development, the usual broadband amplifiers The D-class has long ceased to be exotic.
Benefits of Class D amplifiers
The goal of audio amplifiers is to transmit the audio input signal to the audio reproduction system at the required volume and power level - accurately, efficiently and with little interference. Audio frequencies are in the range from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, respectively, the amplifier must have a good frequency response over the entire range (or in a narrower region, if we are talking about a speaker with a limited playback bandwidth, for example, a mid-range or tweeter in a multi-band system). Capacities can be different (depending on specific device): milliwatts in headphones, watts in TV sound systems and audio for PCs, tens of watts in home and automobile sound systems, hundreds or more watts in high-power home and live sound systems.
In conventional analog audio amplifiers, linear mode transistors are used to generate an output voltage that accurately scales the input voltage. The voltage transfer coefficient is usually quite high (about 40 dB). If the forward gain is included in the feedback circuit, then the gain of the entire feedback circuit will be large. Feedback in amplifiers is often used, since a large gain in combination with feedback improves the quality of the amplifier: it suppresses distortion caused by nonlinearities in the forward circuit, and reduces noise from the power supply due to the fact that the power supply influence ratio (PSRR) is reduced.
In the usual transistor amplifier output stage transistors provide a continuous output signal. There are many different engineering solutions for audio systems: class A, AB and B amplifiers. In all, even the most efficient, linear output stages, power dissipation is greater than in class D amplifiers. This property of class D amplifiers gives them an advantage in various systems, such how low power dissipation means less heating of the circuit, saves board space, reduces costs and extends battery life in portable devices.